When you import data, you bring data from another source (usually a file) into an existing FileMaker Pro Advanced file.
FileMaker Pro Advanced can import many different file formats. See Supported import/export file formats.
If FileMaker Pro Advanced does not support the format of a particular application, you may be able to export data from that application into a format that FileMaker Pro Advanced supports, and then import that file. For example, FileMaker Pro Advanced does not import Microsoft Access files, but you could export the data from Microsoft Access to Microsoft Excel, and then import that file.
The source file does not need to have the same number of fields in the same order as the FileMaker Pro Advanced target file. During the import process, you can choose the target fields so that the source data imports into the correct fields, and you can skip fields that you don't want to import.
Note To create a new FileMaker Pro Advanced file from another file format, see Converting a data file to a new FileMaker Pro Advanced file.
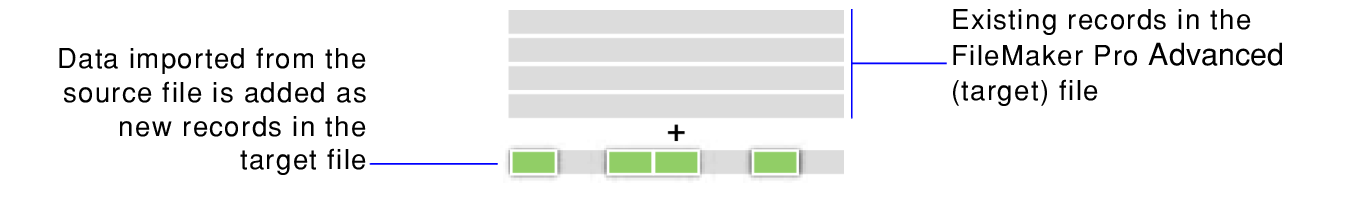
There are three ways to import data into an existing file:
•add new records to the file
•update matching records in the file
•replace existing records in the file
These options, described below, are available in the Import Field Mapping dialog box when you import data into an existing file. See Importing data into an existing file.
Important The options that update or replace records overwrite data in the target file and cannot be undone. To safeguard your data, choose File menu > Save a Copy As to make a backup copy of the target FileMaker Pro Advanced file. You can do this only for a local file (located on your computer).
When you add records, the import process creates a new record in the target file for each importable record in the source file and imports the fields you select.
When you add records from most source file formats, the import process adds all the records from the source file.

When you update matching records, matching records and fields in the target file are updated with data from the source file. For example, you might have a copy of a database on your desktop computer and another copy on your laptop computer. You can update the file in your office with the changes you make on the road.
You determine which records in the source file update which records in the target file by choosing one or more match fields in each file. If data in the match field(s) of a record in the target file matches data in the match field(s) of a record in the source file, the record in the target file will be updated with data from the source file.
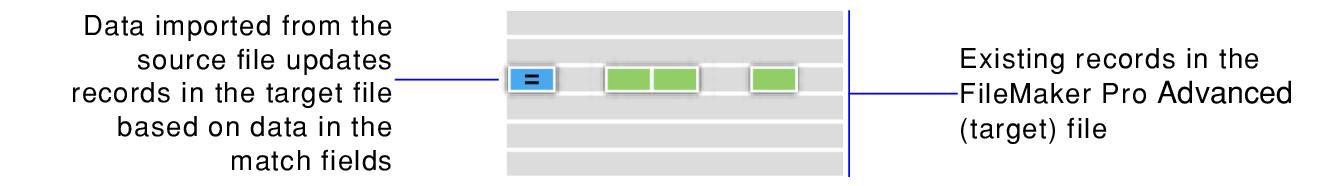
Match fields must uniquely identify each entity in your database. For example, in a database of people, you could use one match field such as an Employee Number, or multiple match fields such as Last Name, First Name, and Phone Number. (Using Last Name alone might identify more than one person, so it isn't a good match field to use by itself.)
You also select which fields to import. The contents of all fields you select, in all matching records, will overwrite data in the target file, even if the field in the source file is blank.
When the target file contains a found set, only the found records are updated.
The following table shows an example of how a record in a target file appears before and after being updated by a matching record in a source file. In the Mapping column, Match Field indicates a match field, Import indicates to import the field, and Don't Import indicates not to import the field.
Source file | Mapping | Target file | Result |
123-456-7890 | Match Field | 123-456-7890 | 123-456-7890 |
John | Don't Import | John | John |
Q | Import |
| Q |
Smith | Don't Import | Smith | Smith |
456 New Rd. | Import | 123 Main St. | 456 New Rd. |
Newtown | Import | Anytown | Newtown |
USA | Import | USA | USA |
| Don't Import | 3/3/1960 | 3/3/1960 |
| Import | (408) 555-6789 |
|
When you replace existing records, data in the target file is replaced with data from the source file. For each field you import into, data from the first importable record (or row of data) in the source file overwrites fields in the first record in the target file. Data from the second importable record (or row of data) in the source file overwrites fields in the second record in the target file, and so on. When you replace data, FileMaker Pro Advanced doesn't examine or compare the data in the files.
You can choose whether or not to replace data on a field-by-field basis.
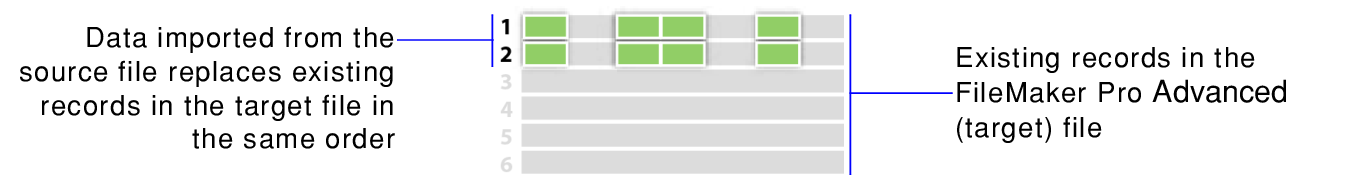
Records in the target file are replaced with the same number of records from the source file. If there are more importable records in the source file, data from the extra records in the source file will not be imported unless you also choose Add remaining data as new records. If there are more records in the target file, data in the extra records in the target file will not be replaced.
•You can only import data into a single table at a time. To import data into related fields, import data directly into the table that contains the related field.
•If the source file is a FileMaker Pro Advanced file with multiple tables, you can only import data from a single table at a time. To import fields from related tables, import directly from the table that contains the field.
•If the source file is a FileMaker Pro Advanced file, you can import only the records in the found set and skip importing the omitted records. See FileMaker Pro format.
•To ensure that imported data is correctly formatted, you can define fields so that data is validated as it is imported. During import, data is skipped when it does not conform to the validation options you set. See About validating data during import.
•If you routinely import data from the same source, you can automate the process by setting up recurring imports or by creating a script that uses the Import Records script step. See Setting up recurring imports and Automating tasks with scripts.