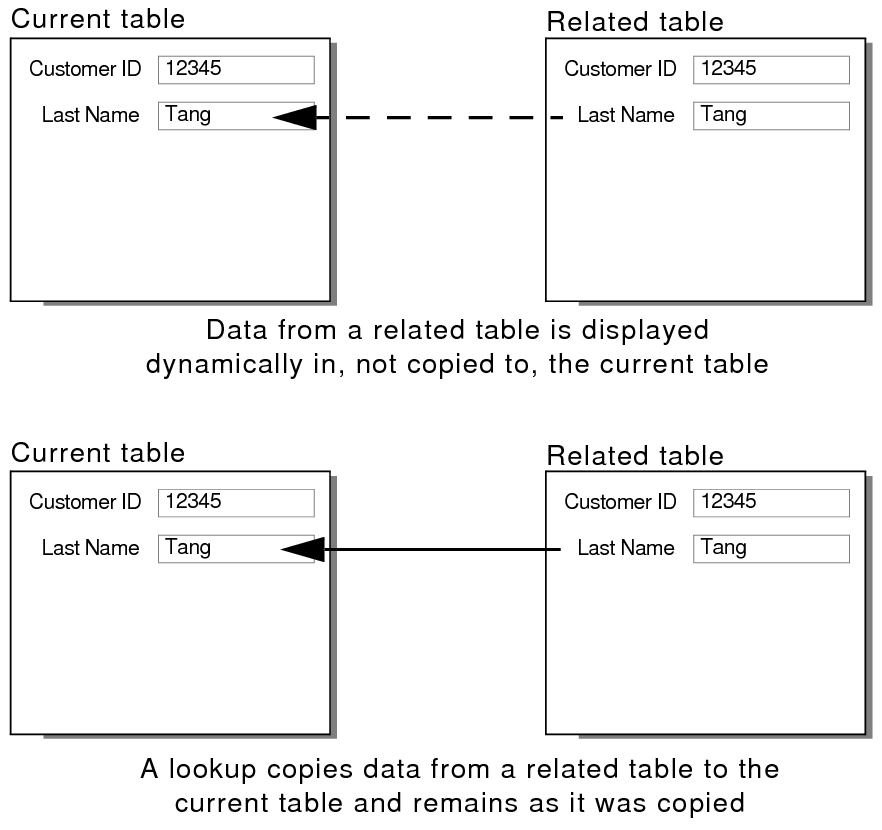
You can create a relational database to allow you to work with data from other tables. A relational database consists of one or more related tables that, when used together, contain the information you need. Each instance of data is stored in only one table at a time but can be accessed and displayed from any related table. You can change any instance of your related data, and the changes appear dynamically in all places. This means that when you change the data in one place, that data is changed wherever it appears, so your data is always up-to-date. Relational databases allow you to work with data in its most current state, set up and manage data efficiently and with flexibility, and save disk space.
To retrieve data from a related table and copy it to the current table, define a lookup. The copied data is now stored in two places, just as if it were copied and pasted into a target field. Looked-up data is current at the time it is copied, but once copied it remains static unless it is looked up again. See Defining and updating lookups.

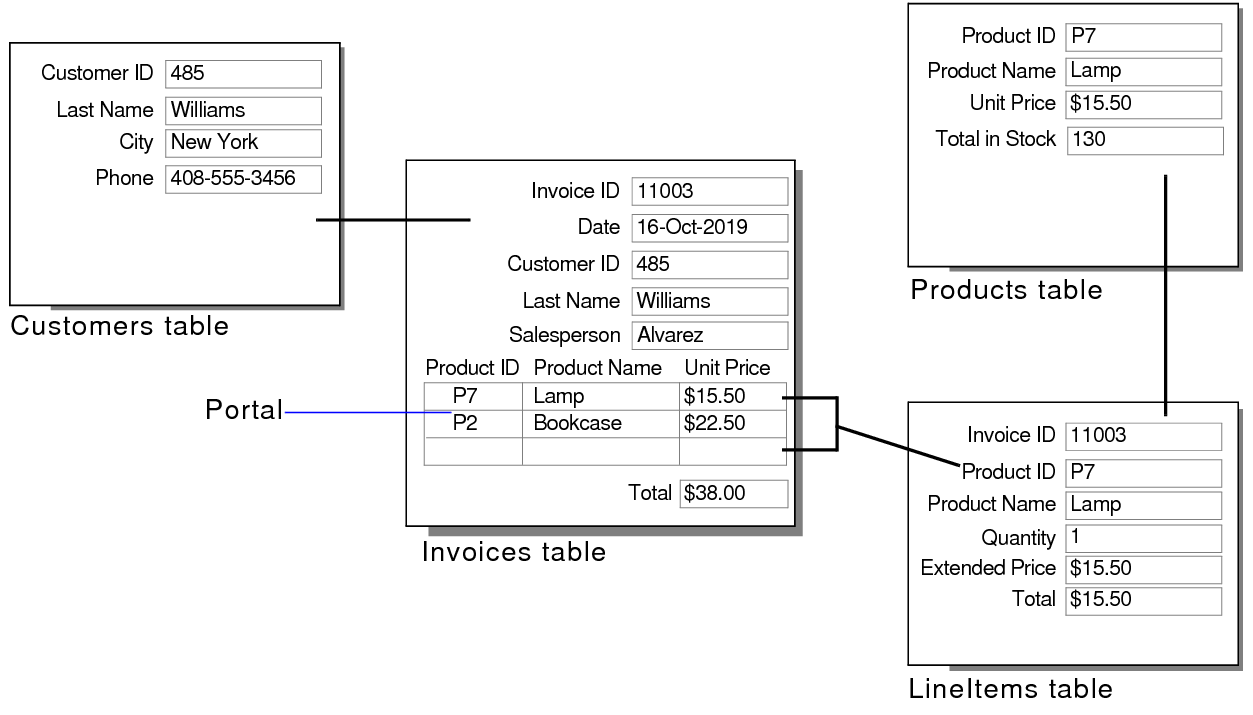
For example, a typical Sales solution may have these tables:
•Customers, which stores customer information such as customer names and contact information
•Products, which stores information about products and their current prices
•LineItems, which stores sales data for each line of an invoice, including the item sold, the quantity, and the price at which it is sold
•Invoices, which keeps a record of each invoice; information displayed in each record comes from related records in the Customers and LineItems tables
Because invoices are a mixture of dynamic data and static data, you use related fields and lookups to display your data. Data from related records in Customers is displayed dynamically on the layout in Invoices. Data from Products is displayed in LineItems. The sales price of each line item is static, and is entered from LineItems into a portal on the Invoices layout using a lookup so that totals in the invoice remain unchanged if the prices of the items change in LineItems later.
Before you begin building a relational database, it’s important to plan it first. See Planning a relational database.
•To see how related tables work with other elements in a FileMaker Pro Advanced solution, visit this page (English).
•A related table can be in the same file or in an external data source.